Technology Vulnerability Management Process with EASM
Modern cybersecurity solutions allow you to partially automate vulnerability management, making it less tedious and more efficient. Let’s explore these optimizations.
When a major security vulnerability is publicly disclosed, thousands of security engineers across the globe dedicate their day to the same task: manually finding where in their organization’s infrastructure they use the vulnerable technology and remediating the vulnerability or mitigating the risks.
There are several major problems with this process:
- Usually, there is at least some shadow IT in the organization. It’s not in the asset inventory, so it’s not accounted for and won’t be patched whether it’s vulnerable or not.
- While the asset inventory contains information about assets, more often than not it doesn’t contain information about versions of the software used on these assets. So, security or DevOps teams need to manually check whether the version installed on each asset is vulnerable – or not.
- The manual process takes a lot of time and effort.
You can avoid all these problems by relying on external attack surface management platforms that can automate at least some parts of the vulnerability management process.
Let’s use CVE-2023-44487 (a high severity vulnerability in Nginx, with CVSS severity score of 7.5 and listed on the Known Exploited Vulnerability catalog) as an example issue and Attaxion as an example EASM platform to show how to do it. For the purpose of this post, let’s imagine that CVE-2023-44487 has just been disclosed and the security team is tasked with urgent remediation across the organization’s infrastructure.
How to Use EASM Platforms for Vulnerability Management
Let’s quickly review how the formal vulnerability management lifecycle looks.
Below are the 5 steps of vulnerability management:
- Asset inventory and vulnerability assessment.
- Vulnerability prioritization.
- Vulnerability remediation or risk mitigation.
- Vulnerability reporting.
- Continuous vulnerability monitoring.
Asset Management & Vulnerability Scanning
EASM platforms like Attaxion continuously scan your external attack surface for new internet-facing assets. This means that at every moment in time you have an up-to-date asset inventory. Since EASM platforms discover both known and unknown assets, they help solve the problem with shadow IT – it gets out of the shadow and becomes known to the IT and security teams.
That covers a part of step 1 of the vulnerability management process and also addresses the shadow IT problem.
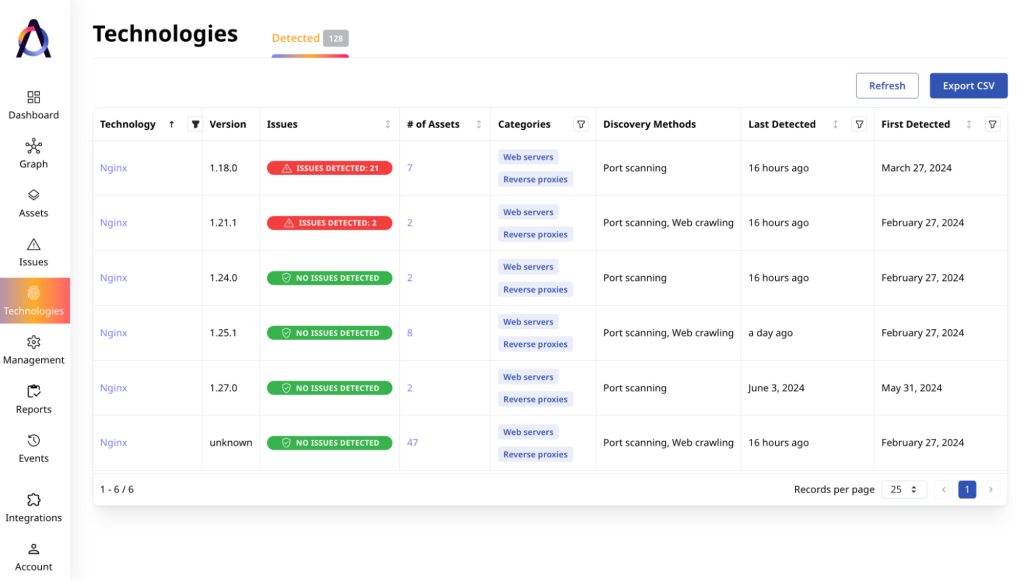
The next thing to do is to look across the entire attack surface for assets that use the vulnerable technology – in our example it’s Nginx.
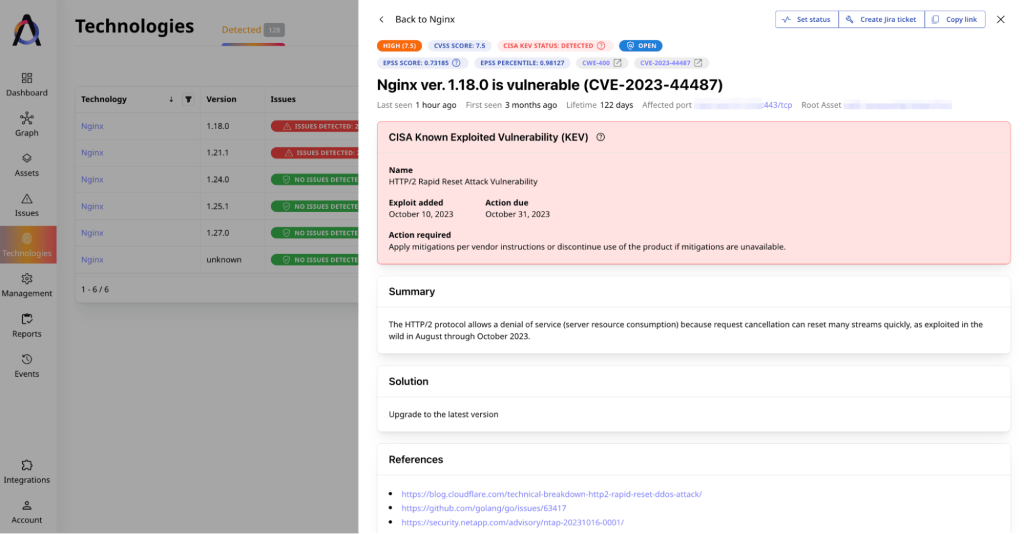
Advanced EASM platforms build an inventory not only of assets, but of technologies as well. For instance, in Attaxion you can find it under the “Technologies” tab. And the only thing the security team needs to do to get a list of all the assets that use Nginx is to go there and filter that list for “Nginx.”
Attaxion can do this – and even sort it by versions. This way, we can clearly see how many vulnerable versions of Nginx we have and how many assets use these versions.
Attaxion EASM solves the second half of step 1 of the vulnerability management process for us – we don’t need to manually check Nginx versions. Attaxion runs a vulnerability scanner and scans both known and newly added assets for vulnerabilities. So, it has already identified all the assets that have this specific vulnerability for us. Basically, Attaxion covers the vulnerability assessment without any human intervention.
In this case, we need to focus on versions 1.18.0 and 1.21.1 – they are vulnerable to CVE-2023-44487. Attaxion shows that they are vulnerable, marking them with red.
Clicking on “1.18.0” gives us a list of the assets in the infrastructure with this specific version of Nginx. There are 7 of them in our example.
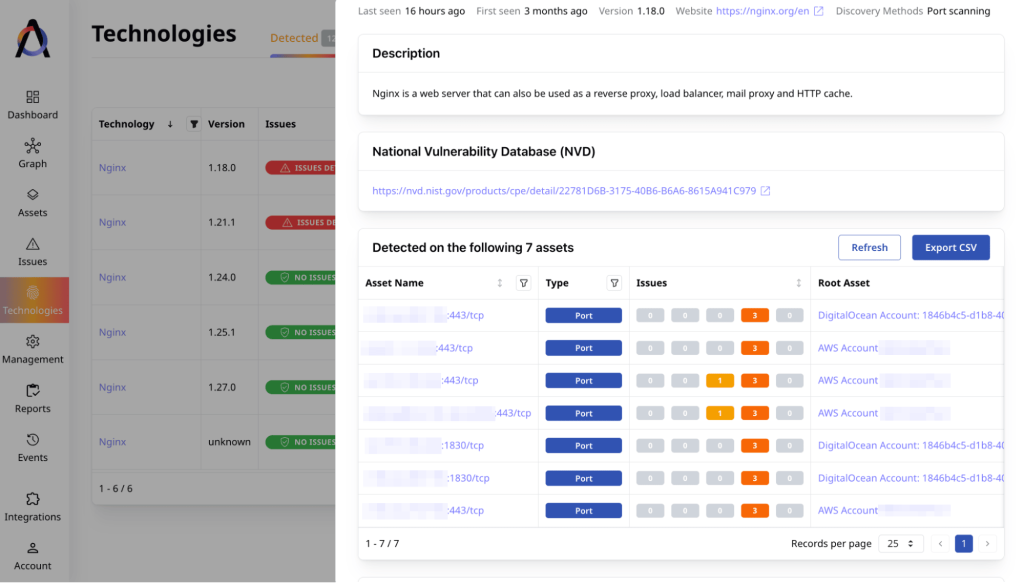
Vulnerability Prioritization and Reporting
It’s time to jump to step 2 of the vulnerability management process and prioritize the vulnerable assets by their criticality for business operations (if we are sticking to the more advanced, risk-based vulnerability management, that takes this into account).
Our example EASM, Attaxion, doesn’t have this functionality (and most of the others also don’t, as they are EASMs, not vulnerability management platforms). But it has tags – and we can use them to assign priorities.
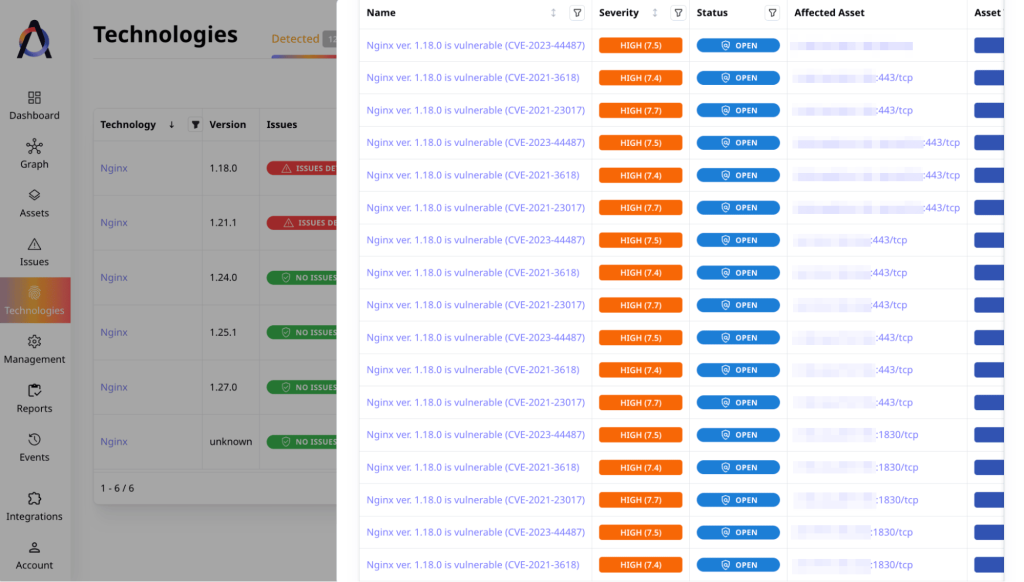
In the same screen, we can see all the issues that these 7 assets have, if we want to patch something else while we’re up to it. We know that we’re looking for CVE-2023-44487, so let’s search for it.
We have narrowed it down to 7 issues. Using the tags that we added, we can prioritize the vulnerability remediation on these assets. Also, we can export a report in a CSV format about these vulnerabilities.
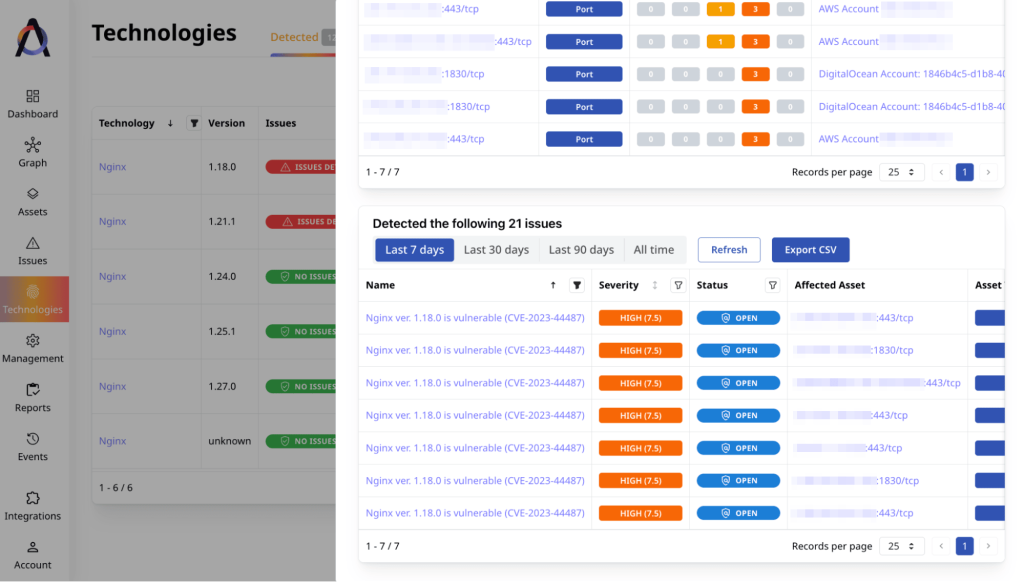
Vulnerability Remediation
If we click on a vulnerability in this list, we’ll see details: what the issue is and what to do about it. In our case, it says we need to update Nginx. It also says that it’s a CISA KEV (Known Exploited Vulnerability), providing insight into when the exploit became available.
EASM platforms cannot roll out updates for us. But they can create support tickets in bug trackers such as Atlassian Jira with all the information about the issues to support our remediation efforts. We’ll need to have an integration with Jira configured to do that.
If the integration is set up, we only need to click a button saying “Create Jira ticket” and then confirm our intentions.
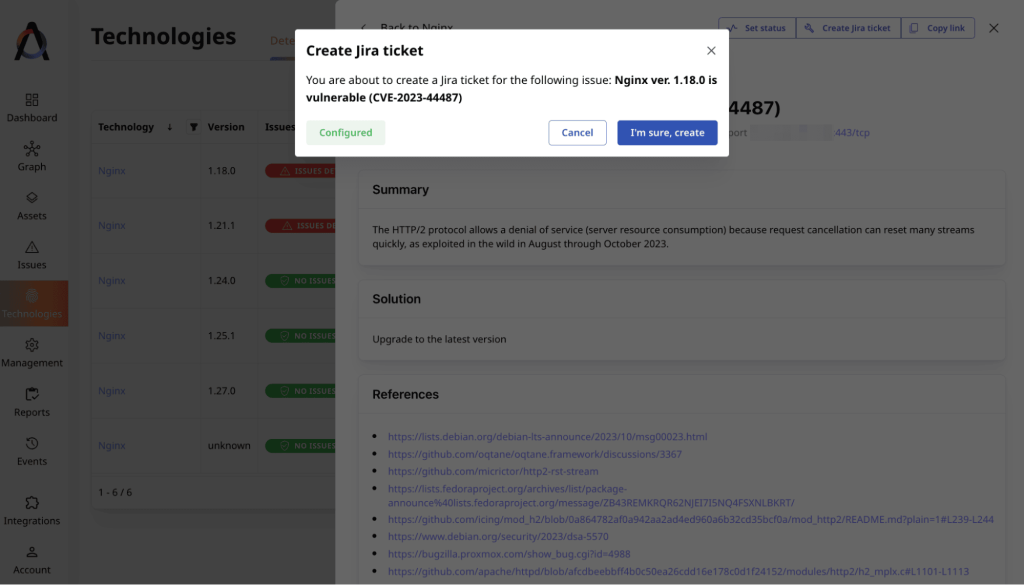
Repeating this process for the Nginx vulnerabilities that Attaxion has found for us will get us 7 new tickets in Jira for the support engineers to update Nginx.
Continuous Vulnerability Monitoring
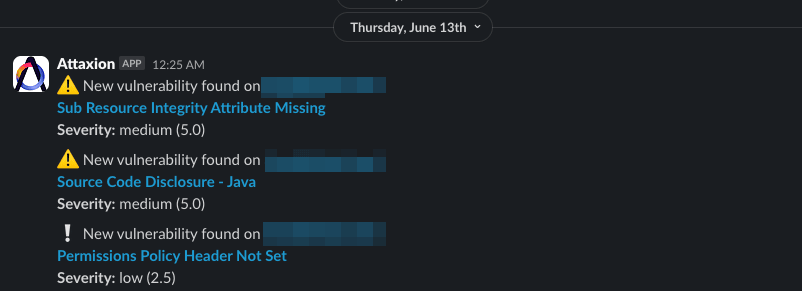
EASM platforms keep scanning the organization’s attack surface continuously. So, if an EASM platform discovers a new asset that is vulnerable, it will notify us about it. In the case with Attaxion, we can use either email or Slack to receive such notifications.
Conclusion
In our example, we have shown how an EASM platform such as Attaxion simplifies the vulnerability management process.
It allows you to quickly assess the scale at which a new issue impacts your organization, prioritize the issues depending on the asset’s business criticality, and create support tickets for the engineers with all the necessary information.
And since vulnerability management is a continuous process, EASM platforms help with maintaining your asset inventory up-to-date and finding new issues. Relying on an EASM, you can build an effective vulnerability management program without extending your security budget to buy expensive vulnerability management tools.

