17 Best Exposure Management Platforms
Ever since Gartner coined the term “continuous threat exposure management (CTEM)” in 2022 and encouraged organizations to build CTEM programs, many cybersecurity vendors have adapted their platforms to support exposure management.
Finding the best exposure management platform for your needs can be a difficult task, though, as many vendors have different ideas of what an exposure management platform should offer. Many solutions are actually vulnerability management or attack surface management (ASM) platforms that have evolved to meet broader exposure management needs.
So, how do you choose the right exposure management software solution? This post explains the features you may want to consider and provides a short overview of some of the top exposure management platforms.
Table of Contents
 INTRO
INTRO
The Five Stages of CTEM
It would be easier to understand what features an exposure management platform needs to have if we first take a look at the CTEM process and its stages. There are five:

- Scoping
Define what matters. Decide which assets, business processes, and attack surfaces should be in focus right now.
Key question: What should be in scope and why? - Discovery
Find the exposures. Continuously map all visible and hidden assets, vulnerabilities, and misconfigurations within that scope.
Key question: Where are we exposed? - Prioritization
Rank by real-world risk. Score each exposure for exploitability plus business impact to decide what needs fixing first.
Key question: Which exposures matter most to us? - Validation
Prove it can happen. Test whether attackers could actually exploit the exposure and whether your controls would stop them.
Key question: Can the bad thing really happen? - Mobilization
Fix and learn. Coordinate security, IT, and business owners to remediate, accept, or transfer the risk—and use the lessons learned to define the next scope.
Key question: Are we fixing it quickly and measurably?
Essential Features of an Effective Exposure Management Platform
Based on how the CTEM process works, this is what an exposure management platform needs to have in order to effectively help with the process:
- Comprehensive asset discovery and inventory: An effective exposure management platform must accurately identify internet-facing assets, including public-facing web servers, APIs, domains, subdomains, SSL certificates, IP addresses, open ports, and services. But it doesn’t stop there. Organizations must also identify assets related to the SaaS applications they’re using, such as cloud instances, user accounts, and any data stored within those applications.
- Continuous exposure assessment: Exposure management is not a one-time event. The platform should continuously monitor and assess assets for vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and other security weaknesses through methods like automated scanning and the use of real-time intelligence feeds.
- Risk-based prioritization: Given the sheer number of potential exposures, an effective exposure management platform must prioritize risks based on their impact and exploitability. For instance, many platforms take into account the Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS) scores and CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog when ranking vulnerabilities. Another aspect that matters is the asset’s business criticality, but no platform can automatically identify what’s really critical for your specific business, so this usually becomes a manual task.
- Remediation guidance: A good exposure management platform should provide actionable guidance on how to remediate exposures, including steps for patching and configuring controls. This guidance should be easily available to the engineers responsible for remediation, even if they don’t have access to the platform itself.
- Integrations: Best security exposure management tools integrate seamlessly with existing security tools and IT infrastructure, such as vulnerability scanners, CMDBs, SIEMs, SOAR platforms, identity and access management (IAM) systems, and ticketing systems.
- Visualization and reporting: It’s important to clearly communicate exposures to stakeholders. An exposure management solution must enable organizations to do so by offering clear and intuitive visualization through customizable dashboards, heatmaps, and various reporting options.

Top Exposure Management Vendors and Platforms
1. Attaxion
Attaxion is an advanced cybersecurity platform that supports CTEM. It automatically discovers external-facing assets and continuously scans them for vulnerabilities. It stands out for having the widest coverage of internet-facing assets, detecting web applications, domains, IP addresses, cloud resources, and even exposed email addresses.
Attaxion offers competitive prices, with its Starter plan priced at $129 per month, which includes up to 40 assets. You get a two-month discount if you pay annually. Attaxion also offers a 30-day free trial.

Attaxion Pros
- Agentless – doesn’t require agents to be deployed on target systems.
- Has some of the top external asset discovery capabilities on the market.
- Identifies malicious traffic to and from your assets using NetFlow data.
- Uses multiple industry-standard threat intelligence feeds and scoring systems to inform risk prioritization (e.g., CVSS, EPSS, CISA KEV).
- Visualizes asset-to-asset relationships and dependencies to help users understand potential attack paths.
Attaxion Cons
- Due to its agentless nature, Attaxion is not designed to detect internal assets.
- It offers essential integrations for Jira, Slack, and major public cloud providers, but the overall integration count is limited compared to other enterprise platforms.
- Reports may offer less customization.

2. CrowdStrike Falcon Exposure Management
CrowdStrike Falcon Exposure Management is a module within the broader Falcon platform. What makes the platform stand out is its use of the Falcon agent to discover internet-facing assets across endpoints and cloud workloads, allowing it to identify both internal and external assets.
CrowdStrike’s pricing page shows four Falcon bundles, with Falcon Go priced at $59.99 per device and Falcon Enterprise at $184.99 per device. However, Falcon Exposure Management is not included in any of those bundles, so the prices may go up if you add the Exposure Management module. The module requires at least one bundle to work, so the costs add up. CrowdStrike offers a 15-day free trial.

CrowdStrike Falcon Exposure Management Pros
- Visibility across endpoints and cloud assets through a single agent.
- AI-driven insights help reduce alert fatigue and focus on critical threats.
- Good for organizations already invested in the CrowdStrike ecosystem.
CrowdStrike Falcon Exposure Management Cons
- Can be expensive, especially for smaller organizations or those that don’t use CrowdStrike.
- Setup and configuration might be complex for new users due to the platform’s breadth.
- Sensor maintenance issues have been noted for the broader Falcon platform.

3. Cymulate Exposure Validation Platform
Cymulate’s Exposure Validation Platform focuses on breach and attack simulations (BAS) in production environments for organizations to continuously test and optimize security controls. The platform also includes automated red teaming.
Cymulate offers a 14-day trial period, but there’s no published pricing on its website. However, its Amazon listing states that the Cymulate Exposure Validation Attack Scenario Package costs $10,000 per month for up to 1,000 attack scenarios in one tenant.

Cymulate Exposure Validation Platform Pros
- Simulates a wide range of attack scenarios, including ransomware, APTs, MITRE ATT&CK techniques, and known CVEs to test security controls.
- Integrates into existing testing frameworks thanks to an open API.
- Has a user-friendly GUI that helps with reporting.
Cymulate Exposure Validation Platform Cons
- Some users report difficulties when integrating Cymulate with other security solutions like SIEMs, EDRs, threat intelligence platforms, and other solutions.
- Lower external attack surface coverage than what top-tier EASM solutions offer.
- May require a lot of backend work to tune alerts.
- May be complex to navigate and operate, especially for beginners or teams with limited staff.
- Cost is per device or tenant, so it can quickly become even more expensive than $10k/month.

4. Picus Exposure Validation
Picus Exposure Validation is a feature within the Picus Security platform that allows users to perform BAS and automated penetration testing. Picus utilizes live attack simulations to assess whether a vulnerability is truly exploitable and assigns an “Exposure Score” after testing the vulnerabilities.
Picus offers a 14-day free trial but does not publish its prices on the website. However, an Amazon listing for Picus Security Validation Platform shows that the entry bundle costs $150,000.00 per year.

Picus Exposure Validation Pros
- The Picus Exposure Score (PXS) reflects the actual exploitability of a vulnerability within the organization’s environment.
- Detailed and actionable reporting, although some users say that the reports page is not very stable.
- Offers many integrations, including ticketing tools, cyber threat intelligence platforms, EDR, SIEM, zero-trust applications, EASM systems, and data loss prevention solutions.
Picus Exposure Validation Cons
- Initial setup can be overwhelming due to the variety of elements.
- EASM visibility is lower than what some other platforms offer.
- Primarily focused on validating existing controls, rather than initial vulnerability discovery.
- Pricing can be too high.

5. Qualys VMDR
Qualys is primarily a vulnerability management solution with exposure management features, such as risk-based prioritization based on real-time threat intelligence. It offers continuous asset discovery, vulnerability assessment, and automated generation of tickets as a part of vulnerability response.
Qualys offers a 30-day free trial and, like the other vendors, does not have a published pricing page. It does have an Amazon listing, though, that shows various VMDR packages, starting at $596 a month for 128 hosts. The most expensive package is for 5,120 hosts, at $6,805 per month.
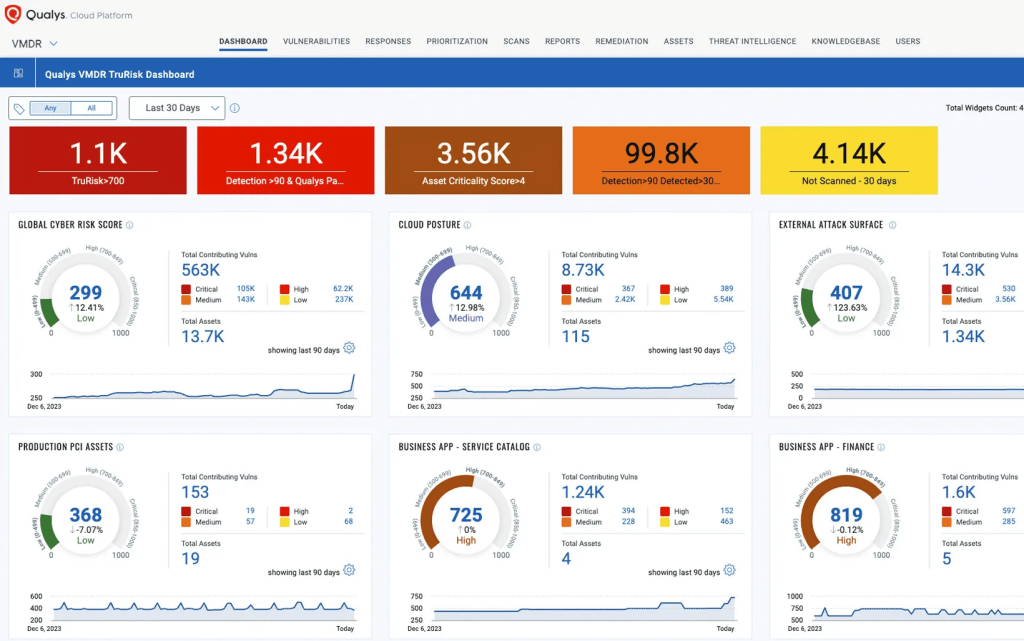
Qualys VMDR Pros
- Easy agent deployment.
- Offers a real-time alert system for critical vulnerabilities.
- Allows users to select and customize the types of scans they need.
- Includes compliance reporting.
- Has connectors for 27 third-party integrations, including Jira, VMware, IBM QRadar, and ServiceNow.
Qualys VMDR Cons
- Users have reported being concerned about false positives and false negatives.
- Pricing can become high as the number of assets increases.
- The platform’s interface is somewhat old-fashioned and can be complex.

6. Tenable One
Tenable One is a unified exposure management platform that consolidates Tenable products, including Vulnerability Management, Cloud Security, Web App Security, OT Security, Identity Security, and ASM. It also includes connectors that allow users to integrate data from third-party security tools.
You have to request a customized quote to learn how much Tenable One Exposure Management costs, but to give some perspective, a one-year subscription for Tenable Vulnerability Management, a component of Tenable One, costs $5,488 for 100 assets. Another component, Tenable Web App Scanning, is priced at $7,056 per year for five FQDNs. Since Tenable One includes seven products, the cost can quickly add up.
There is no free trial period published for Tenable One, but there’s a seven-day free trial for Tenable Nessus Expert – another part of the platform that covers EASM.

Tenable One Pros
- Consolidates data from IT, cloud, web, OT, and identity environments into a single platform.
- Focuses on attack path analysis, helping identify true business risks.
- Offers many integrations and reporting features.
- Excellent for demonstrating risk posture to executive leadership.
Tenable One Cons
- Initial setup can be complex.
- Less accessible to small organizations because of its high price point.
- Most effective when bundled with other Tenable solutions, which adds to the cost.
- Custom reporting is limited.

7. XM Cyber
As a CTEM platform, XM Cyber identifies and prioritizes exploitable attack paths to an organization’s critical assets by simulating attacker behavior across hybrid environments (on-prem and multi-cloud) to reveal how misconfigurations, identity exposures, and vulnerabilities can be chained together to compromise assets and systems.
Pricing for XM Cyber is typically by quote and depends on the scope of the environment and the features required. There’s no public offer for free trials, nor do they publicly list fixed pricing plans. However, some users have commented on the high licensing costs.

XM Cyber Pros
- Performs BAS, significantly reducing the number of vulnerabilities to fix by prioritizing the most likely to be exploited.
- Offers continuous monitoring and real-time alerts.
- Easy to implement compared to other similar platforms.
XM Cyber Cons
- Requires a high level of administrative effort to operate.
- Customization has to be done in configuration files and not directly on the interface.
- Some users report that the platform can’t detect advanced application vulnerabilities.

Other Notable Exposure Management Platforms
Above, we’ve listed just a few platforms that support CTEM. There are many more that cover at least some parts of the process, including the following:
- Bitsight: Offers an exposure management solution comprising EASM, supply chain exposure, and cyber threat intelligence.
- CyCognito: An EASM platform with organization structure mapping that automatically classifies assets based on business context, helping users assess asset criticality.
- Rapid7 Exposure Command: A hybrid exposure management platform that comes with SOAR and compliance management capabilities on its advanced tier.
- Balbix: A cyber risk management platform that comes with exposure management capabilities like mapping exposures to TTPs.
- Microsoft Security Exposure Management: Microsoft’s version of an exposure management platform, which consolidates insights from other products, such as Microsoft Defender, Microsoft Secure Score, and Microsoft Entra ID.
- Ionix: Offers an exposure validation platform that performs non-intrusive exploit simulations and attack path mapping to prioritize risks.
- SentinelOne Singularity™ Platform: Offers an exposure management component that provides enterprise-wide visibility, risk prioritization for vulnerabilities, and attack path analysis across endpoints, cloud, and identity.
- Ivanti: Delivers an exposure management solution that combines 10 Ivanti products with different focus areas, such as application security posture, EASM, patch management, risk-based vulnerability management, endpoint management, and remote connections security.
- Wiz: Offers a vulnerability management platform specifically designed for cloud environments.
- Pentera: Primarily a security validation platform that supports CTEM adoption through attack surface assessment and security testing.

Conclusion
Continuous threat exposure management is a broad cybersecurity approach that covers a wide variety of functionalities, processes, and approaches. No single vendor may be able to offer everything organizations need to fully implement CTEM, although almost all of them already leverage AI and machine learning and offer automation.
However, when it comes to core exposure management functionalities, the solutions overlap and differ in their approaches. For instance, Attaxion focuses on agentless external attack surface discovery, providing visibility into internet-facing assets at a more affordable price than most tools listed above. Its risk-based vulnerability assessment incorporates real-world exploit intelligence, just as other exposure management platforms do, yet at a fraction of their price.
On the other hand, Picus and Cymulate focus more on exposure validation through BAS and security testing, but these solutions cost tens of thousands of dollars per month, making them inaccessible to smaller enterprises.
Tenable One appears to address the most critical aspects of exposure management, but it also comes at a very hefty price, suitable only for organizations with large cybersecurity budgets.