Risk-based vulnerability management is a cybersecurity process that aims to smartly reduce attack surfaces by letting users prioritize and remediate vulnerabilities that pose the greatest risk to their organizations first. That means security teams sort vulnerabilities according to how critical they are, the likelihood they would be exploited, and the business impact in case an attack succeeds.
Risk-based vulnerability management goes beyond traditional vulnerability management methods, where security teams mostly focus on identifying, assessing, and remediating weaknesses.
Table of Contents
- What Is the Difference between Threat, Vulnerability, and Risk?
- How Do You Implement Risk-Based Vulnerability Management?
- What Is the Difference between Risk-Based Vulnerability Management and Vulnerability Management?
- What Benefits Does Risk-Based Vulnerability Management Provide?
- What Challenges Can Come with Risk-Based Vulnerability Management?
What Is the Difference between Threat, Vulnerability, and Risk?
Before diving deep into risk-based vulnerability, it’s essential to specify the difference between a threat, a vulnerability, and a risk. These terms are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings in the context of security.
What is a vulnerability?
Vulnerabilities are weaknesses or flaws in an asset’s design, implementation, or operation that could serve as an entry point for attackers. They could include weak passwords, software bugs, and unpatched systems. In a way, vulnerabilities can be considered internal factors that organizations have a certain level of control over.
What is a threat?
Threats refer to potential actors, actions, or events that could lead to vulnerability exploitation and cause harm to a target asset or system. Examples of threats include phishing and malware attacks. Though threats commonly come from outside an organization, they may also come from the inside as employees may abuse privileged access to steal or alter information or damage systems.
What is a risk?
A risk refers to the likelihood that a threat could occur and result in vulnerability exploitation. Risk takes into account both threats and vulnerabilities. Therefore, a vulnerability alone does not pose a security risk unless a threat can exploit it. And since organizations do not have direct control over threats, they rely on vulnerability management techniques to minimize risks.
How to Calculate and Prioritize Risks
When calculating risks, you’re basically calculating the potential impact a security incident might have. So, there are various factors to take into account:
- How business-critical is the asset? Vulnerabilities in critical assets pose higher risks to the organization, so business criticality plays an important role in risk assessment.
- How severe is the vulnerability? Critical vulnerabilities pose higher risks, while medium or low-severity vulnerabilities are less risky to leave. In traditional risk-based management, high-risk vulnerabilities need to be remediated first. However, in the risk-based vulnerability management approach, that’s only one of the factors.
- How probable is the potential threat? The threat landscape changes continuously, with new threats emerging and old threats becoming less frequent. That information is available in the threat intelligence feeds.
- What is the acceptable level of risk? Each organization has its own risk level that is considered acceptable. This threshold is calculated based on factors such as resources required to remediate the risk, impact on the business processes and continuity, and the impact on reputation.
How Do You Implement Risk-Based Vulnerability Management?
Below are some of the basic steps required to implement the risk-based approach to vulnerability management.
- Asset inventory: Start by cataloging all assets and categorizing them based on how critical they are to business operations. External attack surface management (EASM) tools are very useful for this, as they help discover both known and unknown assets and catalog them.
- Vulnerability scanning: Check the assets for vulnerabilities using predetermined vulnerability intelligence sources and tools. The tools used at this stage are vulnerability scanners and yet again EASM platforms.
- Risk assessment: Determine how to evaluate how risky each vulnerability is. You can do that by developing a vulnerability risk assessment matrix, a visual tool that can help determine how likely a vulnerability could be exploited, along with its business impact.
- Vulnerability prioritization: Rank the vulnerabilities based on the results obtained from the previous steps to identify the most risky ones. Some EASM tools can do that automatically based on their own vulnerability scoring systems, but that’s mostly useful for legacy vulnerability management. For the risk-based approach, it’s likely a manual task because external systems cannot properly determine asset criticality for your business.
- Vulnerability remediation: Allocate resources to mitigate the vulnerabilities that present the most significant risk first.
Since the volume of assets and vulnerabilities that comprise attack surfaces continues to grow and evolve, the process is ideally a never-ending cycle.
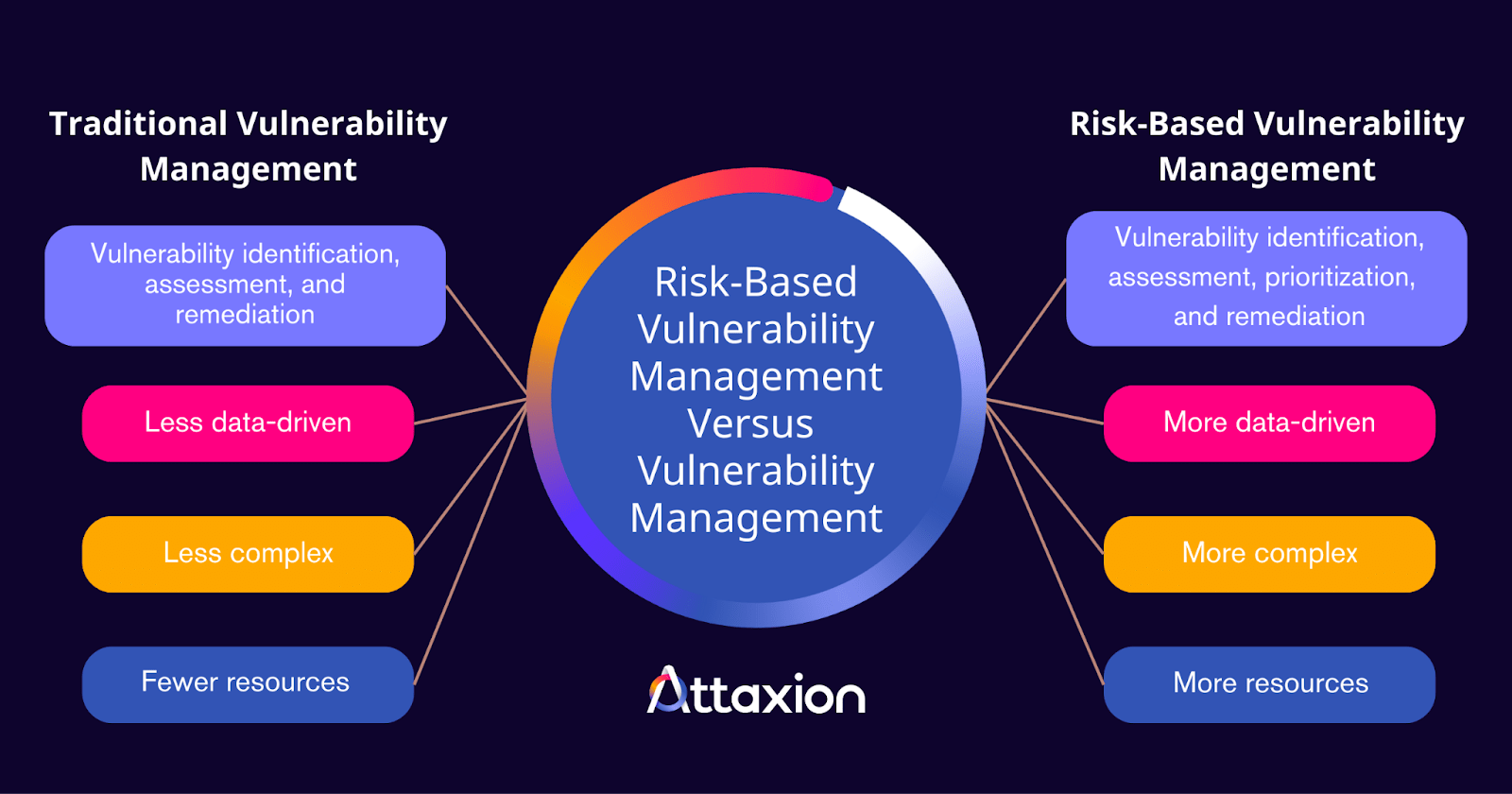
What Is the Difference between Risk-Based Vulnerability Management and Traditional Vulnerability Management?
Risk-based vulnerability management is a more sophisticated and strategic approach than legacy vulnerability management. While both have the same goal, they differ in focus, vulnerability prioritization, resource requirements, and other aspects.
Traditional vulnerability management identifies, assesses, and remediates vulnerabilities, primarily relying on vulnerability scanning tools. Risk-based vulnerability management, meanwhile, adds a crucial step to the process by prioritizing vulnerabilities based on organizational risk.
Risk-based vulnerability management requires an in-depth analysis of misconfigurations, bugs, and other issues and what each means in an organization’s context. As such, it is more complex and requires more resources, but it is also more effective in fighting against modern cyber attacks.
The table below summarizes the primary differences between risk-based vulnerability management and traditional vulnerability management.
What Benefits Does a Risk-Based Vulnerability Management Program Provide?
Risk-based vulnerability management enables effective prioritization. Below are some of its specific benefits.
- Efficient resource allocation: Organizations can better optimize their use of limited resources by focusing remediation efforts on the riskiest vulnerabilities first instead of spending a lot of time on less critical weaknesses.
- Targeted attack surface reduction: Entities can minimize the chances of a successful cyber attack by eliminating the most critical attack vectors specifically designed to target their systems and networks first.
- Improved security posture: By addressing vulnerabilities that pose the greatest risk, organizations strengthen their cybersecurity posture. They avoid risking industry-specific security breaches that could be costly to remediate.
- Regulatory compliance: The process helps organizations minimize cyber risks and avoid security incidents that could result in regulatory noncompliance and penalties or sanctions.
What Challenges Can Come with Risk-Based Vulnerability Management?
While implementing the security process has several advantages, some challenges come with it, too. Below are some of them.
- Risk assessment complexity: To accurately prioritize vulnerabilities based on risk, entities need to collect and analyze massive amounts of data, which can be complex and time-consuming.
- Incomplete asset inventory: Organizations constantly add new systems, applications, and devices to their infrastructure, making asset inventory challenging. That can affect vulnerability analysis and prioritization.
- Insufficient vulnerability data: Obtaining updated and comprehensive vulnerability data can be challenging amid today’s continuously evolving security landscape. But it is a must to avoid incorrect vulnerability prioritization.
—
Despite the challenges that come with implementing risk-based vulnerability management, it helps improve cybersecurity posture and reduces the likelihood of successful cyber attacks.
Key Takeaways
- Risk-based vulnerability management enables companies to prioritize and remediate the vulnerabilities that pose the greatest risk first.
- It is a sophisticated approach that involves the cyclical process of asset inventory, vulnerability scanning, risk assessment, vulnerability prioritization, and vulnerability remediation.
- It differs from traditional vulnerability management in that it focuses on organizational risk rather than issue severity.
- It enables efficient resource allocation, attack surface reduction, security posture enhancement, and regulatory compliance.
- The challenges in implementing the process include risk assessment complexity, maintaining an up-to-date asset inventory, and gathering comprehensive and current vulnerability data.
Ready to learn more about how Attaxion can help? Schedule a customized demo now.
